
How to Select a Diamond
Diamonds are the strongest mineral known to man and are composed entirely of carbon. Diamonds were created under the Earth at depths of 150 to 200 kilometers and at very high levels of temperature and pressure which brought about a process called crystallization in which a carbon crystal is made into a diamond. The diamond is considered a natural treasure and is a leading gemstone.
The value of a diamond is determined by using the 4Cs
Carat

Carat, which relates to the stone's weight.
The heavier the stone, the more it is worth generally speaking.
Clarity

The clarity of a diamond relates to whether it has inclusions, or flaws, on its surface and inside it. Most diamonds have flaws. If the diamond has inclusions it will command a lower price because its clarity is reduced. Scratches, or blemishes on the exterior of a diamond also has an effect on the clarity. The diamond industry generally accepts the following levels of clarity.
FL
A diamond which does not have any flaws inside it, or surface blemishes. Such diamonds are extremely rare and, consequently, are the most expensive.
IF
IF stands for Internally Flawless. The diamond does not have any flaws inside it, but may have some surface blemishes.
VVS1-VVS2
The next gradation is VVS, or Very Very Slightly Included of which there are two grades. The diamond has tiny inclusions which are very difficult to detect without a 10x magnification by a trained gemologist.
VS1-VS2
Next down is Very Slightly Included of which there are also two grades. So small are these inclusions that they can only be seen with difficulty using 10x magnification.
SI1-SI3
This means Slightly Included, and again there are two grades. This size of inclusion can be more easily seen using 10x magnification.
I1-3
Finally, there are inclusions which are big enough to be seen using 10x magnification and even the human eye.
Cut
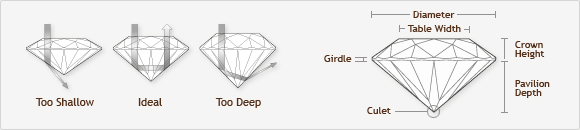
A diamond's cut is critical for a diamond because it determines the brilliance of the diamond. A perfect cut allows light to enter the stone through the table (the top flat part of the diamond) and go on to the pavilion (the lower angled part) where it is completely reflected back through the table. A poor cut means that light is not reflected entirely – and for the buyer that means the stone does not have as much fire, brilliance and sparkle.
Color

The color of a diamond is crucial because it determines whether a diamond sparkles brilliantly and also has a vital role in its price. Diamonds that do not have any color are the most valuable because they allow the largest amount of refraction of light, which gives the diamond its sparkle.
Because a diamond is also a prism – it breaks light down into its spectrum and reflects it back to the eye of the viewer in flashes. Off white diamonds, which contain some yellow or brown, do not absorb light as well and do not allow light to reflect as well, either. Consequently, the diamond's brilliance is much lower.
In regular, or white, diamonds, there is an almost universally agreed way of grading – by using the Gemological Institute of America's color scale. Logically, this should start with an A for best, but in the diamond world it starts with D. A diamond with a D-grade means it has no color and therefore is very valuable because the percentage of such diamonds from global production is very low. From D, the color grade goes down the alphabet, according to the light yellow or brown color, and goes down to Z as you can see from this diagram.
The grades D, E, F are considered the very best and, therefore, command very high prices. Meanwhile, the colors S, T, U, V, W, X, Y, Z, are light yellow or brown shades.
Fancy color diamonds are considered the rarest of stones and have a different category of color from normal, white, diamonds.
Fancy color diamonds have the following categories: Faint; V. Light; Fancy Light; Fancy; Intense; Vivid.
The highest and most expensive color level is Vivid and indicates a very strong color hue.
Diamond Make – this is very important because this heavily influences the brilliance of the light that leaves the diamond.
Diamonds today are usually sold with a certificate, especially larger stones, which specify the diamond's characteristics according to the 4Cs. These certificates are provided gemological laboratories, with the leading lab being the Gemological Institute of America (GIA).
We regard our mission as being to give consumers all the required information so that they can choose and acquire the exact stone their want in the most informed way which will allow them to save money.
